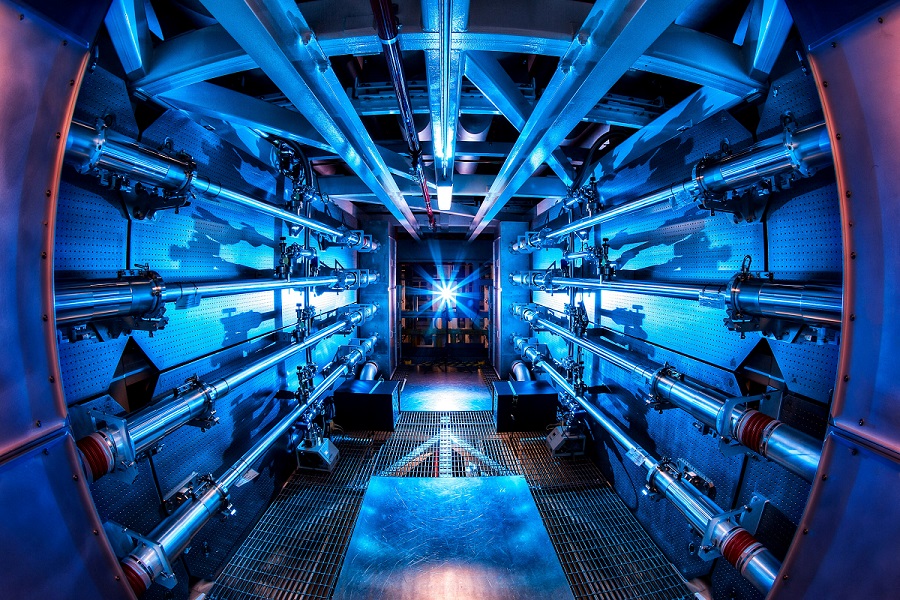
In a groundbreaking achievement, scientists at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in the United States have successfully achieved nuclear fusion ignition multiple times, marking a significant step toward realizing scalable, clean energy sources. The breakthrough, initially accomplished last December and subsequently repeated three times, represents a historic moment in physics.
The team utilized the National Ignition Facility (NIF), employing 192 laser beams to target a frozen pellet of isotopes enclosed within a diamond capsule suspended in a gold cylinder. This process, simulating natural reactions observed in the Sun, resulted in a record energy increase of 89 percent. While the energy produced was currently equivalent to boiling a kettle, the proof-of-concept has the potential to usher in a “new era” of energy, as stated in the scientific journal Nature.
Richard Town, the physicist heading LLNL’s inertial-confinement fusion science program, expressed pride in the achievement, emphasizing its significance. The breakthrough comes amid increasing global interest in nuclear fusion, with discussions at the recent United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) and a commitment by governments to accelerate efforts in fusion technology development.
Noteworthy investments, totaling over $6 billion, have been made by countries including China, Japan, Russia, and the European Union, reflecting the international focus on nuclear fusion research. Tech giant Microsoft has also joined the pursuit, securing the world’s first purchase agreement for this technology earlier in the year.
While LLNL’s success has not yet been replicated by other laboratories, a collaborative effort between the EU and Japan recently inaugurated the JT-60SA reactor in Japan’s Ibaraki Prefecture. This six-storey nuclear fusion reactor aims to achieve fusion ignition in the coming months. Additionally, a larger reactor is currently under construction in France, highlighting the global momentum toward realizing the potential of nuclear fusion as a clean and abundant energy source.







